vaginal cell permeability testing|MINIREVIEWS Porcine Vagina Ex Vivo as a Model for : bulk To control drug retention at the vaginal site, as well as to predict drug absorption, it is highly relevant to determine the permeability of drugs and drug candidates through vaginal . Quem Viu Meu Perfil - Brazilian Dating & Singles at BrazilCu.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webCookies help us improve your website experience. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies.
Vaginal irritation testing—prospects of human organotypic vaginal
Various studies have described the use of ex vivo rabbit vaginal mucosa to test drug permeability. For example, Corbo, Liu, and Chien (1990) tested the transfer of . To develop an in vitro permeability model able to mimic the vaginal environment, it is crucial to include the presence of a mucus layer, SVF, and relevant pH conditions on top of . The in vitro permeability, metabolism, and tissue retention of high/low permeable compounds were assessed on cow vaginal mucosa and compared to the permeabilities .
The most important parameters for vaginal permeability were found to be the relative PSA, logP, logD, water solubility and fraction unbound (FU). Respectively, the combination of both .
Tissue
The Vaginal
To control drug retention at the vaginal site, as well as to predict drug absorption, it is highly relevant to determine the permeability of drugs and drug candidates through vaginal .There is a great deal of data that validates the porcine model of vaginal mucosa in terms of structure, function and reactivity in comparison to human tissue. The use of small, ex vivo, .The characteristics of an ex vivo porcine model are explored and the validity of this model is demonstrated in terms of its histology, ultrastructure and composition and organization of the .
The availability of a reliable primary human cell–based vaginal tissue model narrows the knowledge gap between two dimensional cell-based assays and in vivo irritation, .
The ethical and regulatory requirements pertaining to human participants in research to study the effects of therapeutic agents on genital mucosa have lead to the development of a variety of model systems, including . The growth of stratified, differentiated human vaginal epithelium so as to form organotypic cultures potentially overcomes the disadvantages of cell monolayers. 45 However, in practice it has not proved easy to grow organ . Compared to other two intestinal in vitro permeability models (rat jejunum and Caco-2 cells), vaginal mucosa cannot be used to rank compounds based on drug permeabilities, because physiochemical drug properties (i.e., logP, pH, ionization) seem not to have significant impact on the permeability. Furthermore, substantial physiological .
DOI: 10.1007/s11626-024-00907-1 Corpus ID: 271112644; Vaginal irritation testing-prospects of human organotypic vaginal tissue culture models. @article{Ayehunie2024VaginalIT, title={Vaginal irritation testing-prospects of human organotypic vaginal tissue culture models.}, author={Seyoum Ayehunie and Timothy Landry and Alexander Armento}, journal={In vitro . DSC was used to measure the cell membrane permeabilities of human vaginal macrophages and T cells to water at subzero temperatures, using the approach proposed by Devireddy et al. 21 The results showed that in the temperature-dependent relationship of cell membrane permeability , L pg was 0.0209 μm/atm/min and E a was 41.5 kcal/mol for mucosal .
how do you test a bottle temperature
ASTM D2434: Standard Test Method for Permeability of Granular Soils (Constant Head). Method. Measure the initial mass of the pan along with the dry soil (M 1). Remove the cap and upper chamber of the permeameter by unscrewing the knurled cap nuts and lifting them off the tie rods. Measure the inside diameter of the upper and lower chambers.
The theoretical interpretation of the vaginal permeability phenomenon, the evaluation of the suitability of five artificial membranes, and the prediction of the behaviors of vaginal drugs were the main objectives of this study. Franz vertical diffusion cells and different validated HPLC methods were . The TZM-bl cell line is derived from a HeLa cell clone and was transfected to express CD4, CCR5 and CXCR4 56 and also contain integrated reporter genes for firefly Luciferase and E. coli β . Test of permeability and retention carried out in cell monolayers and pig vaginal mucosa showed different results according to the coating type. Overall, PEO-PCL-NPs were the most effective in increasing microbicide drug residence time at . Constant Head Permeability Test. The Constant Head Permeability Test, also known as the constant head test, analyzes coarse-grained soils like sands and gravels. It maintains a constant hydraulic gradient. VJ Tech’s Clisp Studio Software supports this testing method. In constant head permeability testing, the flow path is designated as “L.”
Tissue. Kits: The EpiVaginal kit VEC-100 contains 24 tissues, VEC-112 contains 12 tissues and VEC-606 contains 6 tissues. (Tissue “kits” contain tissues, a small amount of culture medium, and plasticware; contact MatTek for specific kit contents.) Substrate: Single well tissue culture plate inserts are used. VEC-100: 9 mm individual inserts – tissue culture substrate is chemically .Both primary vaginal cell culture and use of immortalized cell lines have . animal vaginal tissue models are often required in order to draw conclusions regarding comparative human vaginal responses to stimuli or injury, test products, or evaluate devices. . Robinson JR. Vaginal permeability and enzymatic activity studies in normal and .
cellular distribution and permeability. • Viability of tissues treated with the test materials is assessed by MTT. . The most frequently used test to screen for vaginal mucosal irritation is the in vivo rabbit vaginal irritation . results and address many of the shortcomings of current animal and monolayer cell culture test systems. It is(Panel A) Localization of different areas of the oral mucosa where the tissues were extracted to test the permeability of the drugs. (Panel B) Franz Diffusion Cell.(Panel C) Ussing Chamber.(Panel D) Kerski Chamber.Created with BioRender.com (accessed on .19 including integumentary and mucosal (e.g., vaginal) membranes, which are hereinafter called 20 “topical products.” 2 Because of the complex route of delivery associated with these products,
Soil Permeability Testing Equipment. Flexible-Wall Permeability Cells described in ASTM D5084, measure hydraulic conductivity of soils using several methods. The methods within this standard allow several variations on the .
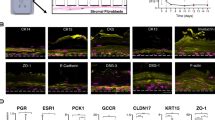
Functional assays confirmed that MPA, but not E2 or P4 treatments, resulted in increased epithelial barrier permeability and inhibited cell cycle progression. The effects of MPA on vaginal epithelial cells seen in this study may help explain the increase of HIV-1 infection in women who use MPA as a hormonal contraceptive.
vertical diffusion cell (VDC) and coining of the term ‘Franz’ diffusion cell (3). The VDC is the most frequently used apparatus to develop and validate IVRT methods. There are other acceptable systems, such as the immersion cell and USP Apparatus 4, but these systems are beyond the scope of this article. TheAbstract. It has been suggested that a triaxial shear test chamber can be used to measure the permeability of low permeability soils. To verify this, the influence of a number of test parameters on the measured coefficient of permeability was investigated. Results indicate such permeability tests should be performed on samples having a minimum diameter of 71.1 mm .
As outlined in ASTM D2434, the soil sample is enclosed in a rigid wall permeameter cell or flexible wall cell that allows water flow through the pores under a hydraulic gradient. . In summary soil permeability testing provides key design criteria for balancing recharge enhancement and controlled drainage based on lawyers of use. Using a microfluidic device, the water permeability (Lp) of vaginal CD3 + T cells and CD14 + macrophages was determined relative to the initial cell volume. The channel height of the microfluidic perfusion chamber was 15 μm to accommodate the monolayer expected cell size of 8–12 μm, and at the edge of the channel the height was 3 μm to .immune cells.25 Recently, studies have shownthatthe presence of a dysbiotic vaginal microbiome is associated with antigen-presenting cells expressing inflammatory genes and pathways including those involved in the interferon response, self/non-self recognition, innate immunity, and T cell-mediated adaptive The membrane potential is relatively stable in non-excitable cells, but in neurons and muscle cells, the membrane potential is quite dynamic, so the membrane potential in a non-excited state is referred to in these cells as the resting potential. The membrane (resting) potential in most animal cells is around -70mV.
CPA exposure tolerance tests for human vaginal mucosal T cells and macrophages. The x-axis shows the final CPA concentration (v/v, %) after addition into the cell suspensions.where V c (t) is the cell volume (μm 3) at time t (min); L p is the cell membrane permeability to water (μm/atm/min); A is the cell membrane area (μm 2) and assumed as constant during perfusion (=4πr 2 for a spherical cell shape); C n i, C n e are the intracellular and extracellular molalities (Osm/kg water), respectively; R is the .
vesting of cervical – vaginal cells collected from women, aged from 22. to 49 years, undergoing hysterectomy. . describe for skin permeability testing, the types of studies (in vivo or. Different approaches have been used to characterize the vaginal permeability of different drugs and other molecules of interest. Methodologies relying on either cell-based three-dimensional organotypic membranes developed in vitro (including some available commercially) or mucosal tissues obtained from animals and women have been proposed .
Objective: To test the biocompatibility of a zinc-containing vaginal gel, evaluate its ability to release zinc, and to assess the transepithelial permeability of zinc on human vaginal epithelium.
Porcine vagina ex vivo as a model for studying permeability and
Resultado da A menos que você tenha uma máquina do tempo, esse conteúdo está indisponível. mucalol transmite ao vivo na Twitch! Confira os vídeos do .
vaginal cell permeability testing|MINIREVIEWS Porcine Vagina Ex Vivo as a Model for